Course 1: Management and Entrepreneurship in CCIs. Syllabus for A&H Students. (C1-AH-STU-EN)

Syllabus for Arts and Humanities (A&H) Students
Course 1 - Management and Entrepreneurship in Cultural and Creative Industries
- UNIT 1: Management and Entrepreneurship in CCIs
- UNIT 2: Entrepreneurial Practice – Modelling a CCI Enterprise

Syllabus for Arts and Humanities (A&H) Students
Course 1 - Management and Entrepreneurship in Cultural and Creative Industries

Syllabus for Arts and Humanities (A&H) Students
Course 1 - Management and Entrepreneurship in Cultural and Creative Industries
Course Description

Introduction
This course is developed within the project “Fostering Entrepreneurship and Innovation in Cultural and Creative Industries through Interdisciplinary Education (FENICE) with the support of the Erasmus+ Programme of the European Union.
It is designed for BA and MA students in arts and humanities (A&H) who want to pursue self-employment or manage creative teams within their careers. In broader terms, the course would be useful for any artist and artist-to-be as it will provide a thorough understanding of the entrepreneurial and management practices that define the modern creative and cultural business. The overall aim is to build the main skills that are needed for career success and creative impact.
The course is interdisciplinary and presents the theory and practice of entrepreneurship and management combining guided and experiential learning activities.
CCIs are content, knowledge and technology-driven and as such, they are, by definition, а subject to interdisciplinary research and education. CCIs combine the creation (often by artists or designers), production (often by companies) and distribution (often by multinationals) of goods and services that are cultural in their nature and usually protected by intellectual property rights.
Developing the entrepreneurial and managerial skills of the students and graduates in the arts and humanities will provide the CCIs with thoughtful, innovative and self-sustainable professionals that can lead and contribute to the viable and sustainable functioning of the creative economy.
Course Objectives/Goals
This course is intended to provide a multi-faceted insight into the operation of CCI enterprises for the students in arts and humanities and to discuss the practical and theoretical issues facing creative and cultural professionals and entrepreneurs. It builds on the interdisciplinary approach that is pertinent to CCIs to showcase how creativity and culture can be sustainably commercialized and bring to life viable and innovative enterprises.
In this sense, the goals of the course are
- To equip students with specific managerial skills that are relevant to the CCIs;
- To improve the entrepreneurial skills and competencies of the students;
- To build students’ capacity in forming and working in cultural and creative teams; solidly anchored in economic realities and up-to-date cultural context;
- To familiarize students with the main important aspects of self-employment in CCIs; such as personal promotion in the on-line environment, organising artistic events and artistic research;
- To prepare students for working in interdisciplinary CCI teams.
Instructional Methods
Considering teaching-learning strategies/methodologies, the main approach in this course is experiential learning. Accordingly, this course makes use of different teaching, learning and assessment methods, in line with the needs of the students and the learning objectives. Teaching methodologies were designed to boost autonomous work while respecting students’ diversity and needs, allowing flexible learning paths.
This course aims at fostering an active learning environment, proven effective in developing higher-order cognitive skills. By being involved in an active and participatory learning process, enhanced by the integration of digital technologies, students intervene directly in the construction of knowledge, questioning and co-creating it. As opposed to conventional approaches, generally passive and unidirectional, the students become the centre of the learning process and the trainer/teacher assumes the role of mediator.
Learning outcomes
Upon the completion of the course, the students should be able to
- Apply concepts related to CCIs, notably when analysing and assessing real-life cases
- Utilize the artistic research methods such as documenting and archiving, trial and error process, presentations, etc.
- Interpret the key characteristics of the economy of the cultural and creative industries, the important challenges the industries face, such as technological, legal and economic – and the policies adopted to meet those challenges
- Develop models for creative business ventures, including strategic planning for entrepreneurship initiatives, innovative methods for generating funds, stakeholder management and development of partnerships, governance structures of creative enterprises, etc.
- Discuss the innovation process in CCIs as an open, interactive, collaborative and interdisciplinary process
- Identify new opportunities within social and business problems and develop business solutions, while at the same time, securing revenue sources that achieving financial sustainability
- Justify the need for business to demonstrate accountability by regularly measuring performance and impact
- Design artistic events (exhibitions, workshops, promotions, etc.) and online promotion campaigns
In addition, the course encourages the implementation of the European Entrepreneurship Competence Framework (EntreComp)[1]. Competencies are presented by area and with reference to whether they are improved (when they are effectively developed within the scope of the contents foreseen for the course) and/or assessed (when subject to evaluation), and with regards to the two content units proposed within this course – Unit 1: Understanding Entrepreneurship in the CCIs and Unit 2: Entrepreneurial Practice – Modelling a CCI Enterprise – which are further detailed in section IV of this syllabus.
[1] http://europa.eu/!kR69Tb
Course content
The contents of the course refer to the following main considerations and rationales in the CCIs:
- Mutual understanding and comprehension between artistic creativity and economics/management, toward feasibility and economic viability of CCI product/project is indispensable. Professionals with both types of profiles need to be aware of the necessity to develop and employ skills for team work and cooperation;
- The development of the creative process is different from its transfer to third parties, therefore each participant in the course is required to acquire a business discipline (to see if it can be implemented in the form of diagrams specific to each artistic discipline);
- The key feature of the creative economy is the transformation of artistic value in economic value; as such all the characteristics that give value to an artistic product will have to be monetized as economic values (thus generating business): uniqueness, non-standardization as impossibility of reproduction, technological process, recognition, copyrights, etc., that is, understanding the artistic product in relation to the market is essential.
- Creativity should be the main tool and competence to work within the CCIs. Usually perceived as a natural ability, individual creativity used in teamwork is able to accelerate the evolutionary pace of ideas within a teamwhen used in project-based team work. . During CCI projects, any type of creativity could be the difference of added value and capacity in a competitive market – thinking outside the box, avoiding clichés, permanent adaptation to contemporary realities - regardless of their nature - cultural, economic, technological.
- Within a CCI project team, all members are/should be creative, although only the ones with artistic background (A & H) are creators, from the point of view of professional skills in artistic transposition technology. The creators are motivated by the contemporary cultural and creative context, by the media exposure of the projects’ end product and obviously by the economic benefits of the CCI activities. Feasibility, economic viability and potential success of the CCI team product can be secured or positively evaluated only through the economic and management expertise provided by the members of the team with economic background. The cultural context should definitely be evaluated constantly together within the team, by both artists and CCI economics/management experts. There is also necessary to have a certain level of comprehension within the CCI team – the access to other one subjectivity /artistic creativity versus economic feasibility – and balance must always be reached for the lasting development of the project.
- Eastern, mainstream stakeholders usually state cultural policies tainted by latency, protochronism and reactionary traditionalism. There are some exceptions however: cultural institutions which are financed through competition CCI projects, private stakeholders with contemporary visions over CCI, young galleries, cultural/artistic hubs, independent galleries, private enterprises as cultural stakeholders/non-government organizations, local authorities interested in new cultural visions for their cities/regions. Stakeholders in cultural policies are either mainstream (state driven, institutionally or financed) or alternative (independent/young galleries, private architecture/design offices, independent cultural festivals, media, galleries, cinema, design, multimedia, etc.).
- The Test of Reality – even before the pandemic, it was obvious that financing CCI is more and more connected with some major subjects – is in improving quality of life, especially within urban environment, ecology, recycling, involvement to generate solutions for social problems, preserving and restoration of cultural heritage. Art for the sake of art is no longer an option for public funding. Media exposure is essential for any CCI activity/projects, such as social platforms, the World Wide Web, online publications, etc.
- Involvement in social activities of education – such as creative workshops, youth creative education. Even in a technological environment, an economic option for added value is creativity, originality, artistic creation inserted within production process and end product.
The contents of the course are divided in two major thematic Units, with specific learning objectives and learning outcomes
Unit 1 learning objective and outcome
Unit 1: Understanding Entrepreneurship in the CCIs
(Concepts and Policy Overview)
Specific learning objective:
- To allow students to comprehend the liaison of CCIs with the other sectors of the economy, their innovation and social innovation potential while focusing on the essence of artistic research, open-science approaches and their practical implementation for artists/creators as well as on the relevant innovative, participatory and interdisciplinary working approaches in the CCIs
Specific expected learning outcomes:
In addition to the generic course goals, Unit 1 will enable the students to
- Understand the CCIs and their position in society and economy;
- Differentiate and select the CCI project types;
- Distinguish the roles in CCI teams and communication channels;
- Recognize ethics issues related to the work and the products of the CCIs;
- Define the key stakeholders related to cultural policies;
- Identify the economic implications of cultural policies;
- Interpret issues pertaining to intellectual property in CCIs;
- Analyze the importance of new digital transposition techniques and contemporary; technologies for CCI products, projects, activities;
- Define the main aspects of the entrepreneurial process.
Unit 2 learning objective and outcome
Unit 2: Entrepreneurial Practice – Modelling a CCI Enterprise
(A rally through the different steps in developing a Business Plan)
Specific learning objective:
- To enhance the students’ understanding of the entrepreneurial process from idea generation to concept development and creation of a venture in CCIs while focusing on cooperation, co-creation and interdisciplinarity, and using business planning as a pedagogical tool.
Specific expected learning outcomes:
In addition to the generic course goals, Unit 2 will enable the students to
- Generate and/or identify a business idea in the CCIs;
- Use facts, theories and concepts from different disciplines/knowledge areas appropriately in formulating solutions to entrepreneurial problems;
- Distinguish relationships among various components of business and its environment;
- Select relevant material, non-material and digital resources needed to turn ideas into action;
- Plan value-creating activity which can be financially sustainable over time;
- Promote CCIs’ activities, products and projects through free (costs and use) communication channels;
- Work with scale models, artefacts, and projects in progress through exposure on social media/social platforms and various sites (this may also include testing scaled or real size models within urban or other environments;
- Collaborate to develop business ideas for the CCIs, in particular with artists and cultural professionals.
General List of Readings
- The Museum of Broken Relationships – Modern Love in 203 everyday objects, by Olinka Vištica and Dražen Grubišić, ed. by Weidenfeld & Nicolson, 2017, Great Britain, ISBN (hardback) 978 1 4746 0549 6.
- Luc Long & Mark Dion, Carnet de fouilles & Lab Book, ed. by Actes Sud & Musée Departamental Arles Antique / Luc Long, Carnet de fouilles, Sous la direction de David Djaoui, Actes Sud & Musée Departamental Arles Antique.
- David Usborne, Foreword by Thomas Heatherwick, Objectivity, Thames & Hudson, London, UK, 2010.
- Jonathan D. Lippincott, Large Scale – Fabricating Sculpture in the 1960s and 1970s, Princeton Architectural Press, New York, 2012.
- Douglas Gunn, Roy Luckett & Josh Sims, Vintage Menswear – A Collection from The Vintage Showroom, 2017, Laurence King Publishing Ltd, London, UK.
- Douglas Gunn & Roy Luckett, The Vintage Showroom – An Archive of Menswear, 2015, Laurence King Publishing Ltd, London, UK.
- Contributors, Author Collective, 60. / Innovators shaping our creative future, Thames & Hudson Ltd, 2009, London, UK
- Neil Spiller & Nic Clear, Educating Architects: How tomorrow's practitioners will learn today, Thames & Hudson, London, UK, 2014
- Tristan Manco, Big Art Small Art, Thames & Hudson, London, UK, 2014
- Rian Hughes, Ideas can be Dangerous, ed. by Fiell
- Inna Alesina, Ellen Lupton, Exploring Materials – Creative Design for Everyday Objects, Princeton Architectural Press, New York, Maryland Institute College of Art, Baltimore, New York, 2010.
- Klanten, Robert, Schulze, Floyd, SARAH ILLENBERGER, published by Gestalten, Berlin, 2011, ISBN 978-3-89955-385-7.
- Llewellyn, Nigel, Williamson, Beth, + contributors, THE LONDON ART SCHOOLS: REFORMING THE ART WORLD, 1960 TO NOW, Tate Publishing, 2015, ISBN 978 1 84976 296 0.
- McLellan, Todd, THINGS COME APART – A Teardown manual for modern living, ed. by Thames & Hudson, London, 2013, ISBN 978-0-500-51676-8.
- Mia, Mini Miss, Yip, Penter, BAG DESIGN – A handbook for accessories designers, ed. by Fashionary International Ltd., 2016, ISBN 978-988-77108-0-6.
- Müller, Bernard, Snoep, Jacomijn Nanette, VOUDOU/VOODOO – The Arbogast Collection, ed. by Éditions Loco/Marc Arbogast, Strasbourg, 2013, ISBN 978-2-919507-16-0.
- Sudjic, Deyan, THE LANGUAGE OF THINGS – Understanding the world of desirable objects, ed. by W. W. Norton & Company, New York, 2009, ISBN 978-0-393-07081-1.
- Abisuga-Oyekunle, O. A. & Fillis, I. R. (2017), The role of handicraft micro-enterprises as a catalyst for youth employment. Creative Industries Journal, 10:1, 59-74, DOI: 10.1080/17510694.2016.1247628
- Aquino, E., Phillips, R., and Sung, H. (2012). Tourism, culture, and the creative industries: Reviving distressed neighbourhoods with arts-based community tourism. Tourism, Culture & Communication, 12(1), 5–18.
- Bakas, F.E., Duxbury, N. & De Castro, V.T. (2018). ‘Creative tourism: Catalysing artisan entrepreneur networks in rural Portugal.’ International Journal of Entrepreneurial Behaviour & Research 24 (4), pp.731-752, https://doi.org/10.1108/IJEBR-03-2018-0177.
- Banaji, S., Burn, A. & Buckingham, D. (2010). The rhetorics of creativity: a literature review. Creativity, Culture & Education.
- Belfiore, E. (2002). Art as a means of alleviating social exclusion: does it really work? A critique of instrumental cultural policies and social impact in the UK. International Journal of Cultural Policy, 8(1), pp. 91-106.
- Bessant, J. & Tidd, J. (2015). Innovation and entrepreneurship (3rd ed). Wiley
- Burry, Mark & Burry, Jane, Prototyping for Architects, Thames & Hudson Ltd., London, 2016
- ClydeBan Business (2016). Business Plan QuickStart Guide: The Simplified Beginner’s Guide to Writing a Business Plan. ClydeBan Media
- Colette, H. (2009). Women and the creative industries: exploring the popular appeal. Creative Industries Journal, 2:2, 143-160, DOI: 10.1386/cij.2.2.143/1
- De Beukelaer, C. & O’Connor, J. (2017). The Creative Economy and the Development Agenda: The Use and Abuse of ‘Fast Policy’. In Polly Stupples & Katerina Teaiwa (eds.), Contemporary Perspectives on Art and International Development (pp. 27-47). Routledge.
- Duxbury, N., Albino, S., & Carvalho, C. (orgs.) (2021), Creative Tourism: Cultural Resources, Entrepreneurship and Engaging Creative Travellers [forthcoming]. CAB International.
- Duxbury, N. & Bakas, F.E. (2020). "Creative Tourism: A Humanistic Paradigm in Practice". In Shaping a humanistic perspective for the tourism industry, edited by Ernestina Giudici; Maria
- Della Lucia; Daniela Pettinao. Book II, chapter 7,Italy: Routledge.
- Finch, B. (2013). How to Write a Business Plan. Kogan Page
- Flew, T. (2012). The Creative Industries. Culture and Policy. Sage.
- Florida, R. (2002). The rise of the creative class... and how it’s transforming work, leisure, community and everyday life. Basic Books
- Gouvea, R., Kapelianis, D., Montoya, M-J. R. & Vora, G. (2020). The creative economy, innovation and entrepreneurship: an empirical examination, Creative Industries Journal, DOI: 10.1080/17510694.2020.1744215
- Kerrigan, S., McIntyre, P., Fulton, J. & Meany, M. (2020). The systemic relationship between creative failure and creative success in the creative industries, Creative Industries Journal, 13:1, 2-16, DOI: 10.1080/17510694.2019.1624134
- Lee-Ross, D. & Lashley, C. (2009). Entrepreneurship and Small Business Management in the Hospitality Industry. Elsevier
- Noyes E., Allen, I. E. & Parise, S. (2012). Innovation and entrepreneurial behaviour in the Popular Music industry. Creative Industries Journal, 5:1-2, 139-150, DOI: 10.1386/cij.5.1-2.139_1
- Osterwalder, A. & Pigneur, Y. (2010). Business Model Generation: A Handbook for Visionaries, Game Changers, and Challengers. John Wiley & Sons
- Richards, G. (2020). Designing creative places: The role of creative tourism. Annals of Tourism Research, 85.
- Richards, G. (2010). Increasing the attractiveness of places through cultural resources. Tourism, Culture & Communication, 10, 47–58.
- Cerneviciute, Jurate & Strazdas, Rolandas. (2018). Teamwork management in Creative industries: factors influencing productivity. Entrepreneurship and Sustainability Issues. 6. 503-516
- Dümcke, C (2015). New Business Models in the Cultural and Creative Sectors (CCSs).
- European Expert Network on Culture
- Koleva, P. (2021), Cross-sectoral cooperation and innovation within Creative and Cultural Industries – practices, opportunities and policies within the area of the Northern Dimension Partnership on Culture, Northern Dimension Partnership on Culture (NDPC)
BG
- Министерство на културата на Република България (2019), Стратегия за развитие на българскиата култура (2019-2029), Проект
- Кабаков, И. (2004), Мениджмънт и правна инфраструктура на културата, София: Сиела, ISBN 9549064298
- Кабаков, И. (2017), Интегрирано управление на културата, София: УИ „Св. Клиемтн Охридски“, ISBN 9789540743127
- Колева, П.Г. (2013), Иновационните практики като фактор за стратегическо развитие на организации в сектор „Култура“, София: Интеркултута Консулт
- Стоянов, И. (2018), Място на творческите индустрии в областните стратегии за развитие — проблеми и възможности, Велико Търново: ВТУ „Св.Св. Кирил и Методйй“, Годишник на департамент „Администрация и управление”, т. 3
- Борисова, В. (2017), Бизнес с интелектуална собственост в творческите индустрии, София:УНСС, ISBN 9786192320034
- Наръчник „Ролята на местните власти за насърчаване на креативните индустрии“ (2016), София: Фондация „Каузи“
- Проект „Дигитална култура за регионално сближаване“, https://www.digital-culture.eu/bg
- Дракър, П. (2010), Практика на мениджмънта, София: Класика и стил, ISBN 9549964167
- Дракър, П. (2002), Ефективното управление, София: Класика и стил, ISBN 9549964167
- Ламиман, Ж. (2003). Успешната иновация, София: Класика и стил
- Бърд, Д (2012), Директен и дигитален маркетинг на здравия разум, София: Locus, ISBN
- 9789547831841
- Тотева, М (2019), Функции на дигитализацията при комуникация 4.0, Сп. „Реторика и комуникации“, брой 39
- Тодоров, П., (2008), Промени в пазара на електронните медии в условията на цифровизация, електронно издание „Медии и обществени комуникации“, бр. 1, декември
PT
- AICEP (2020). Guia de apoio às Indústrias Culturais e Criativas [brief information on the available finantial programmes and support mechanisms]. Available at: https://portugalglobal.pt/PT/ComprarPortugal/Fileiras/industrias-culturais-criativas/Paginas/industrias-culturais-criativas.aspx
- Amaral, N. (2019). Impacto: como comunicar em público. Arena Editora
- Carvalho, J. M. (2016). Inovação e Empreendedorismo (2ª ed). Vida económica
- Duxbury, N., Fortuna, C., Bandeirinha, J. A. & Peixoto, P. (2012). Em torno da cidade criativa. Revista Crítica de Ciências Sociais, 99, pp. 5-8
- Faustino, P. (2014). Indústrias Criativas, Media e Clusters. Media XXI. ISBN: 9789897290572
- Fundação Serralves (2008). Estudo Macroeconómico para o desenvolvimento de um Cluster de Indústrias Criativas na região do Norte. Porto: Fundação Serralves.
- Mateus, A. (Coord.) (2010). O Sector cultural e Criativo em Portugal. Estudo para o Ministério da Cultura. Augusto Mateus & Associados.
- Mateus, A. (Coord.) (2013). A cultura e a criatividade na internacionalização da economia portuguesa. Estudo para o Gabinete de Estratégia, Planeamento e Avaliação Culturais da Secretaria de Estado da Cultura. Augusto Mateus & Associados.
- Quintela, P. & Ferreira, C. (2018). Indústrias culturais e criativas em Portugal: um balanço crítico de uma nova ‘agenda’ para as políticas públicas no início deste milénio. Revista Todas as Artes, 1(1), pp. 89-111, DOI: 10.21747/21843805/tav1n1a6
- Saraiva, J. M. (2015). Empreendedorismo. Do conceito à aplicação, da ideia ao negócio, da tecnologia ao valor (3ª ed). Imprensa da Universidade
- Sarkar, S. (2014). Empreendedorismo e Inovação (3ª ed). Escolar Editora.
SR
- Milena Dragićević Šešić, Sanjin Dragojević (2005). Menadžment umetnosti u turbulentnim okolnostima. ISBN: 953-222-282-0
- Dragićević-Šešić, M. (2012) Ethical dilemmas in cultural policies: conceptualising new managerial practices in new democracies. Zbornik radova Fakulteta dramskih umetnosti, str. 69-94
- Dimitrije Vujadinović (2005). Umetnost i autosko pravo. ISBN: 978-86-84159-25-9
This course is developed within the project “Fostering Entrepreneurship and Innovation in Cultural and Creative Industries through Interdisciplinary Education (FENICE) with the support of the Erasmus+ Programme of the European Union.
It is designed for BA and MA students in arts and humanities (A&H) who want to pursue self-employment or manage creative teams within their careers. In broader terms, the course would be useful for any artist and artist-to-be as it will provide a thorough understanding of the entrepreneurial and management practices that define the modern creative and cultural business. The overall aim is to build the main skills that are needed for career success and creative impact.
The course is interdisciplinary and presents the theory and practice of entrepreneurship and management combining guided and experiential learning activities.
CCIs are content, knowledge and technology-driven and as such, they are, by definition, а subject to interdisciplinary research and education. CCIs combine the creation (often by artists or designers), production (often by companies) and distribution (often by multinationals) of goods and services that are cultural in their nature and usually protected by intellectual property rights.
Developing the entrepreneurial and managerial skills of the students and graduates in the arts and humanities will provide the CCIs with thoughtful, innovative and self-sustainable professionals that can lead and contribute to the viable and sustainable functioning of the creative economy.
This course is intended to provide a multi-faceted insight into the operation of CCI enterprises for the students in arts and humanities and to discuss the practical and theoretical issues facing creative and cultural professionals and entrepreneurs. It builds on the interdisciplinary approach that is pertinent to CCIs to showcase how creativity and culture can be sustainably commercialized and bring to life viable and innovative enterprises.
In this sense, the goals of the course are
- To equip students with specific managerial skills that are relevant to the CCIs;
- To improve the entrepreneurial skills and competencies of the students;
- To build students’ capacity in forming and working in cultural and creative teams; solidly anchored in economic realities and up-to-date cultural context;
- To familiarize students with the main important aspects of self-employment in CCIs; such as personal promotion in the on-line environment, organising artistic events and artistic research;
- To prepare students for working in interdisciplinary CCI teams.
Considering teaching-learning strategies/methodologies, the main approach in this course is experiential learning. Accordingly, this course makes use of different teaching, learning and assessment methods, in line with the needs of the students and the learning objectives. Teaching methodologies were designed to boost autonomous work while respecting students’ diversity and needs, allowing flexible learning paths.
This course aims at fostering an active learning environment, proven effective in developing higher-order cognitive skills. By being involved in an active and participatory learning process, enhanced by the integration of digital technologies, students intervene directly in the construction of knowledge, questioning and co-creating it. As opposed to conventional approaches, generally passive and unidirectional, the students become the centre of the learning process and the trainer/teacher assumes the role of mediator.
Upon the completion of the course, the students should be able to
- Apply concepts related to CCIs, notably when analysing and assessing real-life cases
- Utilize the artistic research methods such as documenting and archiving, trial and error process, presentations, etc.
- Interpret the key characteristics of the economy of the cultural and creative industries, the important challenges the industries face, such as technological, legal and economic – and the policies adopted to meet those challenges
- Develop models for creative business ventures, including strategic planning for entrepreneurship initiatives, innovative methods for generating funds, stakeholder management and development of partnerships, governance structures of creative enterprises, etc.
- Discuss the innovation process in CCIs as an open, interactive, collaborative and interdisciplinary process
- Identify new opportunities within social and business problems and develop business solutions, while at the same time, securing revenue sources that achieving financial sustainability
- Justify the need for business to demonstrate accountability by regularly measuring performance and impact
- Design artistic events (exhibitions, workshops, promotions, etc.) and online promotion campaigns
In addition, the course encourages the implementation of the European Entrepreneurship Competence Framework (EntreComp)[1]. Competencies are presented by area and with reference to whether they are improved (when they are effectively developed within the scope of the contents foreseen for the course) and/or assessed (when subject to evaluation), and with regards to the two content units proposed within this course – Unit 1: Understanding Entrepreneurship in the CCIs and Unit 2: Entrepreneurial Practice – Modelling a CCI Enterprise – which are further detailed in section IV of this syllabus.
[1] http://europa.eu/!kR69Tb
The contents of the course refer to the following main considerations and rationales in the CCIs:
- Mutual understanding and comprehension between artistic creativity and economics/management, toward feasibility and economic viability of CCI product/project is indispensable. Professionals with both types of profiles need to be aware of the necessity to develop and employ skills for team work and cooperation;
- The development of the creative process is different from its transfer to third parties, therefore each participant in the course is required to acquire a business discipline (to see if it can be implemented in the form of diagrams specific to each artistic discipline);
- The key feature of the creative economy is the transformation of artistic value in economic value; as such all the characteristics that give value to an artistic product will have to be monetized as economic values (thus generating business): uniqueness, non-standardization as impossibility of reproduction, technological process, recognition, copyrights, etc., that is, understanding the artistic product in relation to the market is essential.
- Creativity should be the main tool and competence to work within the CCIs. Usually perceived as a natural ability, individual creativity used in teamwork is able to accelerate the evolutionary pace of ideas within a teamwhen used in project-based team work. . During CCI projects, any type of creativity could be the difference of added value and capacity in a competitive market – thinking outside the box, avoiding clichés, permanent adaptation to contemporary realities - regardless of their nature - cultural, economic, technological.
- Within a CCI project team, all members are/should be creative, although only the ones with artistic background (A & H) are creators, from the point of view of professional skills in artistic transposition technology. The creators are motivated by the contemporary cultural and creative context, by the media exposure of the projects’ end product and obviously by the economic benefits of the CCI activities. Feasibility, economic viability and potential success of the CCI team product can be secured or positively evaluated only through the economic and management expertise provided by the members of the team with economic background. The cultural context should definitely be evaluated constantly together within the team, by both artists and CCI economics/management experts. There is also necessary to have a certain level of comprehension within the CCI team – the access to other one subjectivity /artistic creativity versus economic feasibility – and balance must always be reached for the lasting development of the project.
- Eastern, mainstream stakeholders usually state cultural policies tainted by latency, protochronism and reactionary traditionalism. There are some exceptions however: cultural institutions which are financed through competition CCI projects, private stakeholders with contemporary visions over CCI, young galleries, cultural/artistic hubs, independent galleries, private enterprises as cultural stakeholders/non-government organizations, local authorities interested in new cultural visions for their cities/regions. Stakeholders in cultural policies are either mainstream (state driven, institutionally or financed) or alternative (independent/young galleries, private architecture/design offices, independent cultural festivals, media, galleries, cinema, design, multimedia, etc.).
- The Test of Reality – even before the pandemic, it was obvious that financing CCI is more and more connected with some major subjects – is in improving quality of life, especially within urban environment, ecology, recycling, involvement to generate solutions for social problems, preserving and restoration of cultural heritage. Art for the sake of art is no longer an option for public funding. Media exposure is essential for any CCI activity/projects, such as social platforms, the World Wide Web, online publications, etc.
- Involvement in social activities of education – such as creative workshops, youth creative education. Even in a technological environment, an economic option for added value is creativity, originality, artistic creation inserted within production process and end product.
The contents of the course are divided in two major thematic Units, with specific learning objectives and learning outcomes
Unit 1: Understanding Entrepreneurship in the CCIs
(Concepts and Policy Overview)
Specific learning objective:
- To allow students to comprehend the liaison of CCIs with the other sectors of the economy, their innovation and social innovation potential while focusing on the essence of artistic research, open-science approaches and their practical implementation for artists/creators as well as on the relevant innovative, participatory and interdisciplinary working approaches in the CCIs
Specific expected learning outcomes:
In addition to the generic course goals, Unit 1 will enable the students to
- Understand the CCIs and their position in society and economy;
- Differentiate and select the CCI project types;
- Distinguish the roles in CCI teams and communication channels;
- Recognize ethics issues related to the work and the products of the CCIs;
- Define the key stakeholders related to cultural policies;
- Identify the economic implications of cultural policies;
- Interpret issues pertaining to intellectual property in CCIs;
- Analyze the importance of new digital transposition techniques and contemporary; technologies for CCI products, projects, activities;
- Define the main aspects of the entrepreneurial process.
Unit 2: Entrepreneurial Practice – Modelling a CCI Enterprise
(A rally through the different steps in developing a Business Plan)
Specific learning objective:
- To enhance the students’ understanding of the entrepreneurial process from idea generation to concept development and creation of a venture in CCIs while focusing on cooperation, co-creation and interdisciplinarity, and using business planning as a pedagogical tool.
Specific expected learning outcomes:
In addition to the generic course goals, Unit 2 will enable the students to
- Generate and/or identify a business idea in the CCIs;
- Use facts, theories and concepts from different disciplines/knowledge areas appropriately in formulating solutions to entrepreneurial problems;
- Distinguish relationships among various components of business and its environment;
- Select relevant material, non-material and digital resources needed to turn ideas into action;
- Plan value-creating activity which can be financially sustainable over time;
- Promote CCIs’ activities, products and projects through free (costs and use) communication channels;
- Work with scale models, artefacts, and projects in progress through exposure on social media/social platforms and various sites (this may also include testing scaled or real size models within urban or other environments;
- Collaborate to develop business ideas for the CCIs, in particular with artists and cultural professionals.
- The Museum of Broken Relationships – Modern Love in 203 everyday objects, by Olinka Vištica and Dražen Grubišić, ed. by Weidenfeld & Nicolson, 2017, Great Britain, ISBN (hardback) 978 1 4746 0549 6.
- Luc Long & Mark Dion, Carnet de fouilles & Lab Book, ed. by Actes Sud & Musée Departamental Arles Antique / Luc Long, Carnet de fouilles, Sous la direction de David Djaoui, Actes Sud & Musée Departamental Arles Antique.
- David Usborne, Foreword by Thomas Heatherwick, Objectivity, Thames & Hudson, London, UK, 2010.
- Jonathan D. Lippincott, Large Scale – Fabricating Sculpture in the 1960s and 1970s, Princeton Architectural Press, New York, 2012.
- Douglas Gunn, Roy Luckett & Josh Sims, Vintage Menswear – A Collection from The Vintage Showroom, 2017, Laurence King Publishing Ltd, London, UK.
- Douglas Gunn & Roy Luckett, The Vintage Showroom – An Archive of Menswear, 2015, Laurence King Publishing Ltd, London, UK.
- Contributors, Author Collective, 60. / Innovators shaping our creative future, Thames & Hudson Ltd, 2009, London, UK
- Neil Spiller & Nic Clear, Educating Architects: How tomorrow's practitioners will learn today, Thames & Hudson, London, UK, 2014
- Tristan Manco, Big Art Small Art, Thames & Hudson, London, UK, 2014
- Rian Hughes, Ideas can be Dangerous, ed. by Fiell
- Inna Alesina, Ellen Lupton, Exploring Materials – Creative Design for Everyday Objects, Princeton Architectural Press, New York, Maryland Institute College of Art, Baltimore, New York, 2010.
- Klanten, Robert, Schulze, Floyd, SARAH ILLENBERGER, published by Gestalten, Berlin, 2011, ISBN 978-3-89955-385-7.
- Llewellyn, Nigel, Williamson, Beth, + contributors, THE LONDON ART SCHOOLS: REFORMING THE ART WORLD, 1960 TO NOW, Tate Publishing, 2015, ISBN 978 1 84976 296 0.
- McLellan, Todd, THINGS COME APART – A Teardown manual for modern living, ed. by Thames & Hudson, London, 2013, ISBN 978-0-500-51676-8.
- Mia, Mini Miss, Yip, Penter, BAG DESIGN – A handbook for accessories designers, ed. by Fashionary International Ltd., 2016, ISBN 978-988-77108-0-6.
- Müller, Bernard, Snoep, Jacomijn Nanette, VOUDOU/VOODOO – The Arbogast Collection, ed. by Éditions Loco/Marc Arbogast, Strasbourg, 2013, ISBN 978-2-919507-16-0.
- Sudjic, Deyan, THE LANGUAGE OF THINGS – Understanding the world of desirable objects, ed. by W. W. Norton & Company, New York, 2009, ISBN 978-0-393-07081-1.
- Abisuga-Oyekunle, O. A. & Fillis, I. R. (2017), The role of handicraft micro-enterprises as a catalyst for youth employment. Creative Industries Journal, 10:1, 59-74, DOI: 10.1080/17510694.2016.1247628
- Aquino, E., Phillips, R., and Sung, H. (2012). Tourism, culture, and the creative industries: Reviving distressed neighbourhoods with arts-based community tourism. Tourism, Culture & Communication, 12(1), 5–18.
- Bakas, F.E., Duxbury, N. & De Castro, V.T. (2018). ‘Creative tourism: Catalysing artisan entrepreneur networks in rural Portugal.’ International Journal of Entrepreneurial Behaviour & Research 24 (4), pp.731-752, https://doi.org/10.1108/IJEBR-03-2018-0177.
- Banaji, S., Burn, A. & Buckingham, D. (2010). The rhetorics of creativity: a literature review. Creativity, Culture & Education.
- Belfiore, E. (2002). Art as a means of alleviating social exclusion: does it really work? A critique of instrumental cultural policies and social impact in the UK. International Journal of Cultural Policy, 8(1), pp. 91-106.
- Bessant, J. & Tidd, J. (2015). Innovation and entrepreneurship (3rd ed). Wiley
- Burry, Mark & Burry, Jane, Prototyping for Architects, Thames & Hudson Ltd., London, 2016
- ClydeBan Business (2016). Business Plan QuickStart Guide: The Simplified Beginner’s Guide to Writing a Business Plan. ClydeBan Media
- Colette, H. (2009). Women and the creative industries: exploring the popular appeal. Creative Industries Journal, 2:2, 143-160, DOI: 10.1386/cij.2.2.143/1
- De Beukelaer, C. & O’Connor, J. (2017). The Creative Economy and the Development Agenda: The Use and Abuse of ‘Fast Policy’. In Polly Stupples & Katerina Teaiwa (eds.), Contemporary Perspectives on Art and International Development (pp. 27-47). Routledge.
- Duxbury, N., Albino, S., & Carvalho, C. (orgs.) (2021), Creative Tourism: Cultural Resources, Entrepreneurship and Engaging Creative Travellers [forthcoming]. CAB International.
- Duxbury, N. & Bakas, F.E. (2020). "Creative Tourism: A Humanistic Paradigm in Practice". In Shaping a humanistic perspective for the tourism industry, edited by Ernestina Giudici; Maria
- Della Lucia; Daniela Pettinao. Book II, chapter 7,Italy: Routledge.
- Finch, B. (2013). How to Write a Business Plan. Kogan Page
- Flew, T. (2012). The Creative Industries. Culture and Policy. Sage.
- Florida, R. (2002). The rise of the creative class... and how it’s transforming work, leisure, community and everyday life. Basic Books
- Gouvea, R., Kapelianis, D., Montoya, M-J. R. & Vora, G. (2020). The creative economy, innovation and entrepreneurship: an empirical examination, Creative Industries Journal, DOI: 10.1080/17510694.2020.1744215
- Kerrigan, S., McIntyre, P., Fulton, J. & Meany, M. (2020). The systemic relationship between creative failure and creative success in the creative industries, Creative Industries Journal, 13:1, 2-16, DOI: 10.1080/17510694.2019.1624134
- Lee-Ross, D. & Lashley, C. (2009). Entrepreneurship and Small Business Management in the Hospitality Industry. Elsevier
- Noyes E., Allen, I. E. & Parise, S. (2012). Innovation and entrepreneurial behaviour in the Popular Music industry. Creative Industries Journal, 5:1-2, 139-150, DOI: 10.1386/cij.5.1-2.139_1
- Osterwalder, A. & Pigneur, Y. (2010). Business Model Generation: A Handbook for Visionaries, Game Changers, and Challengers. John Wiley & Sons
- Richards, G. (2020). Designing creative places: The role of creative tourism. Annals of Tourism Research, 85.
- Richards, G. (2010). Increasing the attractiveness of places through cultural resources. Tourism, Culture & Communication, 10, 47–58.
- Cerneviciute, Jurate & Strazdas, Rolandas. (2018). Teamwork management in Creative industries: factors influencing productivity. Entrepreneurship and Sustainability Issues. 6. 503-516
- Dümcke, C (2015). New Business Models in the Cultural and Creative Sectors (CCSs).
- European Expert Network on Culture
- Koleva, P. (2021), Cross-sectoral cooperation and innovation within Creative and Cultural Industries – practices, opportunities and policies within the area of the Northern Dimension Partnership on Culture, Northern Dimension Partnership on Culture (NDPC)
BG
- Министерство на културата на Република България (2019), Стратегия за развитие на българскиата култура (2019-2029), Проект
- Кабаков, И. (2004), Мениджмънт и правна инфраструктура на културата, София: Сиела, ISBN 9549064298
- Кабаков, И. (2017), Интегрирано управление на културата, София: УИ „Св. Клиемтн Охридски“, ISBN 9789540743127
- Колева, П.Г. (2013), Иновационните практики като фактор за стратегическо развитие на организации в сектор „Култура“, София: Интеркултута Консулт
- Стоянов, И. (2018), Място на творческите индустрии в областните стратегии за развитие — проблеми и възможности, Велико Търново: ВТУ „Св.Св. Кирил и Методйй“, Годишник на департамент „Администрация и управление”, т. 3
- Борисова, В. (2017), Бизнес с интелектуална собственост в творческите индустрии, София:УНСС, ISBN 9786192320034
- Наръчник „Ролята на местните власти за насърчаване на креативните индустрии“ (2016), София: Фондация „Каузи“
- Проект „Дигитална култура за регионално сближаване“, https://www.digital-culture.eu/bg
- Дракър, П. (2010), Практика на мениджмънта, София: Класика и стил, ISBN 9549964167
- Дракър, П. (2002), Ефективното управление, София: Класика и стил, ISBN 9549964167
- Ламиман, Ж. (2003). Успешната иновация, София: Класика и стил
- Бърд, Д (2012), Директен и дигитален маркетинг на здравия разум, София: Locus, ISBN
- 9789547831841
- Тотева, М (2019), Функции на дигитализацията при комуникация 4.0, Сп. „Реторика и комуникации“, брой 39
- Тодоров, П., (2008), Промени в пазара на електронните медии в условията на цифровизация, електронно издание „Медии и обществени комуникации“, бр. 1, декември
PT
- AICEP (2020). Guia de apoio às Indústrias Culturais e Criativas [brief information on the available finantial programmes and support mechanisms]. Available at: https://portugalglobal.pt/PT/ComprarPortugal/Fileiras/industrias-culturais-criativas/Paginas/industrias-culturais-criativas.aspx
- Amaral, N. (2019). Impacto: como comunicar em público. Arena Editora
- Carvalho, J. M. (2016). Inovação e Empreendedorismo (2ª ed). Vida económica
- Duxbury, N., Fortuna, C., Bandeirinha, J. A. & Peixoto, P. (2012). Em torno da cidade criativa. Revista Crítica de Ciências Sociais, 99, pp. 5-8
- Faustino, P. (2014). Indústrias Criativas, Media e Clusters. Media XXI. ISBN: 9789897290572
- Fundação Serralves (2008). Estudo Macroeconómico para o desenvolvimento de um Cluster de Indústrias Criativas na região do Norte. Porto: Fundação Serralves.
- Mateus, A. (Coord.) (2010). O Sector cultural e Criativo em Portugal. Estudo para o Ministério da Cultura. Augusto Mateus & Associados.
- Mateus, A. (Coord.) (2013). A cultura e a criatividade na internacionalização da economia portuguesa. Estudo para o Gabinete de Estratégia, Planeamento e Avaliação Culturais da Secretaria de Estado da Cultura. Augusto Mateus & Associados.
- Quintela, P. & Ferreira, C. (2018). Indústrias culturais e criativas em Portugal: um balanço crítico de uma nova ‘agenda’ para as políticas públicas no início deste milénio. Revista Todas as Artes, 1(1), pp. 89-111, DOI: 10.21747/21843805/tav1n1a6
- Saraiva, J. M. (2015). Empreendedorismo. Do conceito à aplicação, da ideia ao negócio, da tecnologia ao valor (3ª ed). Imprensa da Universidade
- Sarkar, S. (2014). Empreendedorismo e Inovação (3ª ed). Escolar Editora.
SR
- Milena Dragićević Šešić, Sanjin Dragojević (2005). Menadžment umetnosti u turbulentnim okolnostima. ISBN: 953-222-282-0
- Dragićević-Šešić, M. (2012) Ethical dilemmas in cultural policies: conceptualising new managerial practices in new democracies. Zbornik radova Fakulteta dramskih umetnosti, str. 69-94
- Dimitrije Vujadinović (2005). Umetnost i autosko pravo. ISBN: 978-86-84159-25-9
UNIT 1 has the following Topics/Themes:
- T1.1: Understanding CCIs. Cross-Sectoral Collaborations
- T1.2: Creativity and Innovation. Accountability and Ethical Behavior
- T1.3: Cultural Policies and Institutions. Intellectual Property
- T1.4: Entrepreneurial Mindset and Process
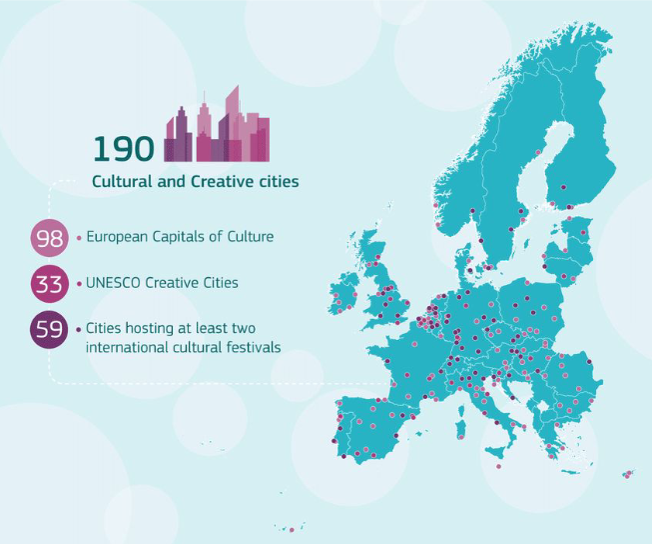 The theme introduces the essence of the cultural and creative industries and their specifics as a fast-developing area of economic activity that fosters economic growth, job creation and export earnings while promoting social inclusion, cultural diversity and human development, especially at the local and regional levels. Attention is placed on interpreting CCIs as interdisciplinary sectors with high knowledge-absorption potential, which however thrive on local resources and heritage.
The theme introduces the essence of the cultural and creative industries and their specifics as a fast-developing area of economic activity that fosters economic growth, job creation and export earnings while promoting social inclusion, cultural diversity and human development, especially at the local and regional levels. Attention is placed on interpreting CCIs as interdisciplinary sectors with high knowledge-absorption potential, which however thrive on local resources and heritage.
- Number of hours: 3 in class, 3 self study.
 In the framework of this theme, types of teams for different areas of CCI are presented and discussed (film production, gaming, event production etc.), including a presentation of particular vocations that make the fabric of a CCI team. In addition, types of CCI projects will be discussed, with the effort to make a distinction between artistic, technical and managerial roles in those projects. What is innovation in terms of CCIs and which team members are the drivers of creativity and innovation in a CCI project? The communication and team management methods applicable to CCI teams will be discussed.
In the framework of this theme, types of teams for different areas of CCI are presented and discussed (film production, gaming, event production etc.), including a presentation of particular vocations that make the fabric of a CCI team. In addition, types of CCI projects will be discussed, with the effort to make a distinction between artistic, technical and managerial roles in those projects. What is innovation in terms of CCIs and which team members are the drivers of creativity and innovation in a CCI project? The communication and team management methods applicable to CCI teams will be discussed.
Special attention will be paid to accountability and ethical behaviour in terms of GDPR CSR (corporate social responsibility), ethical leadership, human rights and employee rights and duties.
- Number of hours: 3 in class, 3 self study.
 The theme is aimed at providing insight into cultural policies, the institutional, administrative and operative aspects of cultural policies, as well as the goals and societal backgrounds that influence cultural policies. Cultural policies are based on an understanding of culture that is specific to the society that created the policy. This, however, needs to be reflected on the global market in which the CCIs exist and the interactions of specific cultural policies and the global market affect the work and aims of CCI projects. The theme will address the issues of the stakeholders that create cultural policies and stakeholders that cultural policies pertain to, defining broadly the channels for effecting change.
The theme is aimed at providing insight into cultural policies, the institutional, administrative and operative aspects of cultural policies, as well as the goals and societal backgrounds that influence cultural policies. Cultural policies are based on an understanding of culture that is specific to the society that created the policy. This, however, needs to be reflected on the global market in which the CCIs exist and the interactions of specific cultural policies and the global market affect the work and aims of CCI projects. The theme will address the issues of the stakeholders that create cultural policies and stakeholders that cultural policies pertain to, defining broadly the channels for effecting change.
Within this theme, information will be provided on the topic of intellectual property in CCIs. The issues of intellectual property in CCIs will be addressed through examples related to designs, copyright and rights related to copyright (for performers, producers and broadcasters).
- Number of hours: 3 in class, 3 self study.
 The theme introduces the concept of entrepreneurship and its interpenetration in view of the CCIs. The basic concepts in the area of entrepreneurship are presented together with the role and importance of entrepreneurship for economic development. Attention is placed on interpreting entrepreneurship as a state of mind and on the main set of skills, competences and knowledge that are needed by an entrepreneur. Issues, such as key steps in the elaboration of business idea, the stages of the entrepreneurial process and the resources needed for the successful development of entrepreneurial ventures, are also covered.
The theme introduces the concept of entrepreneurship and its interpenetration in view of the CCIs. The basic concepts in the area of entrepreneurship are presented together with the role and importance of entrepreneurship for economic development. Attention is placed on interpreting entrepreneurship as a state of mind and on the main set of skills, competences and knowledge that are needed by an entrepreneur. Issues, such as key steps in the elaboration of business idea, the stages of the entrepreneurial process and the resources needed for the successful development of entrepreneurial ventures, are also covered.
- Number of hours: 3 in class, 3 self study.
UNIT 2 has the following Topics/Themes:
- T2.1: Designing a business for the CCIs: preparing a business plan and pitching business
- T2.2: Product or Service from economic point of view. Economic Value. Product and service in arts. Cultural Value
- T2.3: Market, Competition, Consumption and Branding in CCIs
- T2.4: Business models, systems, partnerships
- T2.5: Management: team and change management in the CCIs
- T2.6: Financing. Opportunities and Risks
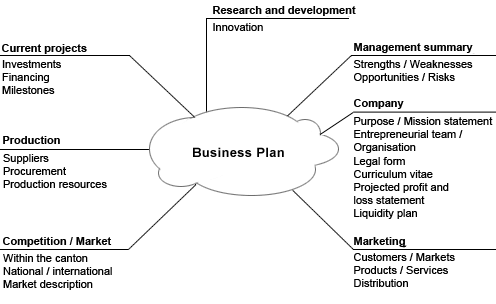 This theme introduces the concept of a business plan as a roadmap that systematises a business, details the business’ operational and financial objectives, determines the viability of a business idea, and guides decision-making. Given the relevance of the business plan when starting a business, which is crucial for the success of a venture in any field of activity and so as in CCIs, special attention is given to the content/key sections of the business plan: products and services (value proposition, key activities, resources), management and control, partnerships, market analysis, marketing strategy, and financial planning (forecasted income and costs, funding needs). Considering relevant communication techniques in business contexts, the role of pitching a business idea is approached. Relevant tips and especial guidance/mentoring on how to prepare and deliver a pitch for potential investors are presented to the students.
This theme introduces the concept of a business plan as a roadmap that systematises a business, details the business’ operational and financial objectives, determines the viability of a business idea, and guides decision-making. Given the relevance of the business plan when starting a business, which is crucial for the success of a venture in any field of activity and so as in CCIs, special attention is given to the content/key sections of the business plan: products and services (value proposition, key activities, resources), management and control, partnerships, market analysis, marketing strategy, and financial planning (forecasted income and costs, funding needs). Considering relevant communication techniques in business contexts, the role of pitching a business idea is approached. Relevant tips and especial guidance/mentoring on how to prepare and deliver a pitch for potential investors are presented to the students.
- Number of hours: 3 in class, 3 self study.
 The theme addresses the contemporary challenges of a value-oriented approach to the design of products and services in the CCIs. Theoretical fundamentals related to value creation are tackled and the specific contents of this theme contribute to a better understanding of differences between cultural value and economic value as socially constructed measures. In face of economic value, the market-based paradigm is explored, considering demand systems, pricing, and willingness-to-pay in the specific context of market behaviour within the CCIs. From a business perspective, students are oriented towards a more efficient justification for product or service design or redesign, considering the supply and demand in the CCIs’ marketplace.
The theme addresses the contemporary challenges of a value-oriented approach to the design of products and services in the CCIs. Theoretical fundamentals related to value creation are tackled and the specific contents of this theme contribute to a better understanding of differences between cultural value and economic value as socially constructed measures. In face of economic value, the market-based paradigm is explored, considering demand systems, pricing, and willingness-to-pay in the specific context of market behaviour within the CCIs. From a business perspective, students are oriented towards a more efficient justification for product or service design or redesign, considering the supply and demand in the CCIs’ marketplace.
- Number of hours: 3 in class, 3 self study.
 Within this theme, the relevance of developing effective competitive strategies in the CCI’s business context are discussed. Pertinent topics such as the definition of target markets, customer acquisition, and the communication of the business proposition as a means to set out a business’ competitive advantage in relation to competitors, are addressed. Students are also encouraged to discuss and reflect upon building a customer base and competition in the CCIs, along with its strengths and weaknesses, hence being able to outline specific and impactful marketing and sales strategies. An overview on brand management, based on tangible and intangible brand values, and on the application of branding strategies to the CCIs, boosted by emerging technologies and communication strategies such as storytelling, is offered. Special emphasis is placed on the potential of Digital Marketing in reaching a global marketplace in a more cost-effective and measurable way, in building two-way communication with the CCIs audiences, and in increasing brand awareness.
Within this theme, the relevance of developing effective competitive strategies in the CCI’s business context are discussed. Pertinent topics such as the definition of target markets, customer acquisition, and the communication of the business proposition as a means to set out a business’ competitive advantage in relation to competitors, are addressed. Students are also encouraged to discuss and reflect upon building a customer base and competition in the CCIs, along with its strengths and weaknesses, hence being able to outline specific and impactful marketing and sales strategies. An overview on brand management, based on tangible and intangible brand values, and on the application of branding strategies to the CCIs, boosted by emerging technologies and communication strategies such as storytelling, is offered. Special emphasis is placed on the potential of Digital Marketing in reaching a global marketplace in a more cost-effective and measurable way, in building two-way communication with the CCIs audiences, and in increasing brand awareness.
- Number of hours: 3 in class, 3 self study.
 Business models and systems in the CCIs are specific and depend on the particular way of value creation. Still the theme will start first with explaining the basic features of business modelling as the general pathway for creation and delivery of value and of business systems as the outlines of the different aspect of business operation. Upon discussing the traditional business models and systems, the ones pertinent to the CCIs shall be presented and explored. CCIs gave rise to many novel developments in this regard - such as crowd-funding/sourcing, e-events, non-formal partnerships, vouchering, etc. – following the decrease in public financing for the arts and cultures after the global financial crisis. These shall be studied in detail in view of their viability prospects, recovery and changes driven by the COVID-19 pandemic which was detrimental to many cultural organisations and individual artists in 2020 and 2021.
Business models and systems in the CCIs are specific and depend on the particular way of value creation. Still the theme will start first with explaining the basic features of business modelling as the general pathway for creation and delivery of value and of business systems as the outlines of the different aspect of business operation. Upon discussing the traditional business models and systems, the ones pertinent to the CCIs shall be presented and explored. CCIs gave rise to many novel developments in this regard - such as crowd-funding/sourcing, e-events, non-formal partnerships, vouchering, etc. – following the decrease in public financing for the arts and cultures after the global financial crisis. These shall be studied in detail in view of their viability prospects, recovery and changes driven by the COVID-19 pandemic which was detrimental to many cultural organisations and individual artists in 2020 and 2021.
- Number of hours: 3 in class, 3 self study.
 This theme will provide general overview of the management process in an enterprise while considering the specifics of the enterprises in the CCIs. The main elements of planning, organization, staffing, leadership and control shall be reviewed and considered with practical examples. The focus is placed on managing the teams regarding co-creation and cooperation among professionals with artistic and non-artistic backgrounds. In that, conflict management is considered. Outside the public companies, many enterprises in the CCIs are either sole proprietorships or very small, which fosters them to partner and work in teams on ad hoc basis which makes team management an even more important task the requires skills. Accordingly, the theme will consider the issue of change management – regarding the changing of teams, but also regarding the fast changing environment in which the CCIs operate as defined by digitalization and globalization.
This theme will provide general overview of the management process in an enterprise while considering the specifics of the enterprises in the CCIs. The main elements of planning, organization, staffing, leadership and control shall be reviewed and considered with practical examples. The focus is placed on managing the teams regarding co-creation and cooperation among professionals with artistic and non-artistic backgrounds. In that, conflict management is considered. Outside the public companies, many enterprises in the CCIs are either sole proprietorships or very small, which fosters them to partner and work in teams on ad hoc basis which makes team management an even more important task the requires skills. Accordingly, the theme will consider the issue of change management – regarding the changing of teams, but also regarding the fast changing environment in which the CCIs operate as defined by digitalization and globalization.
- Number of hours: 3 in class, 3 self study.
 The theme will cover the basic elements of planning and managing finance within an enterprise. The main sources of financing, financial sustainability and pricing of products and services shall be considered and discussed via practical cases and examples. On this ground, the fund generation forms that are specific for the CCIs shall be regarded along the main dichotomy of (i) public/governmental funding and (ii) private funding within and beyond philanthropy, including the novel models associated with crowd-sourcing, multi-donor supports, project-based activities and so on. Lastly, the theme shall regard the different types of financing instruments regarding the development stage of an enterprises as well as the risks and opportunities that accompany them. Relevant links shall be made to all the other themes in the course regarding in particular the dichotomy between proprietary and free access sharing of content.
The theme will cover the basic elements of planning and managing finance within an enterprise. The main sources of financing, financial sustainability and pricing of products and services shall be considered and discussed via practical cases and examples. On this ground, the fund generation forms that are specific for the CCIs shall be regarded along the main dichotomy of (i) public/governmental funding and (ii) private funding within and beyond philanthropy, including the novel models associated with crowd-sourcing, multi-donor supports, project-based activities and so on. Lastly, the theme shall regard the different types of financing instruments regarding the development stage of an enterprises as well as the risks and opportunities that accompany them. Relevant links shall be made to all the other themes in the course regarding in particular the dichotomy between proprietary and free access sharing of content.
- Number of hours: 3 in class, 3 self study.
Calendar
Announcements
- - There are no announcements -
